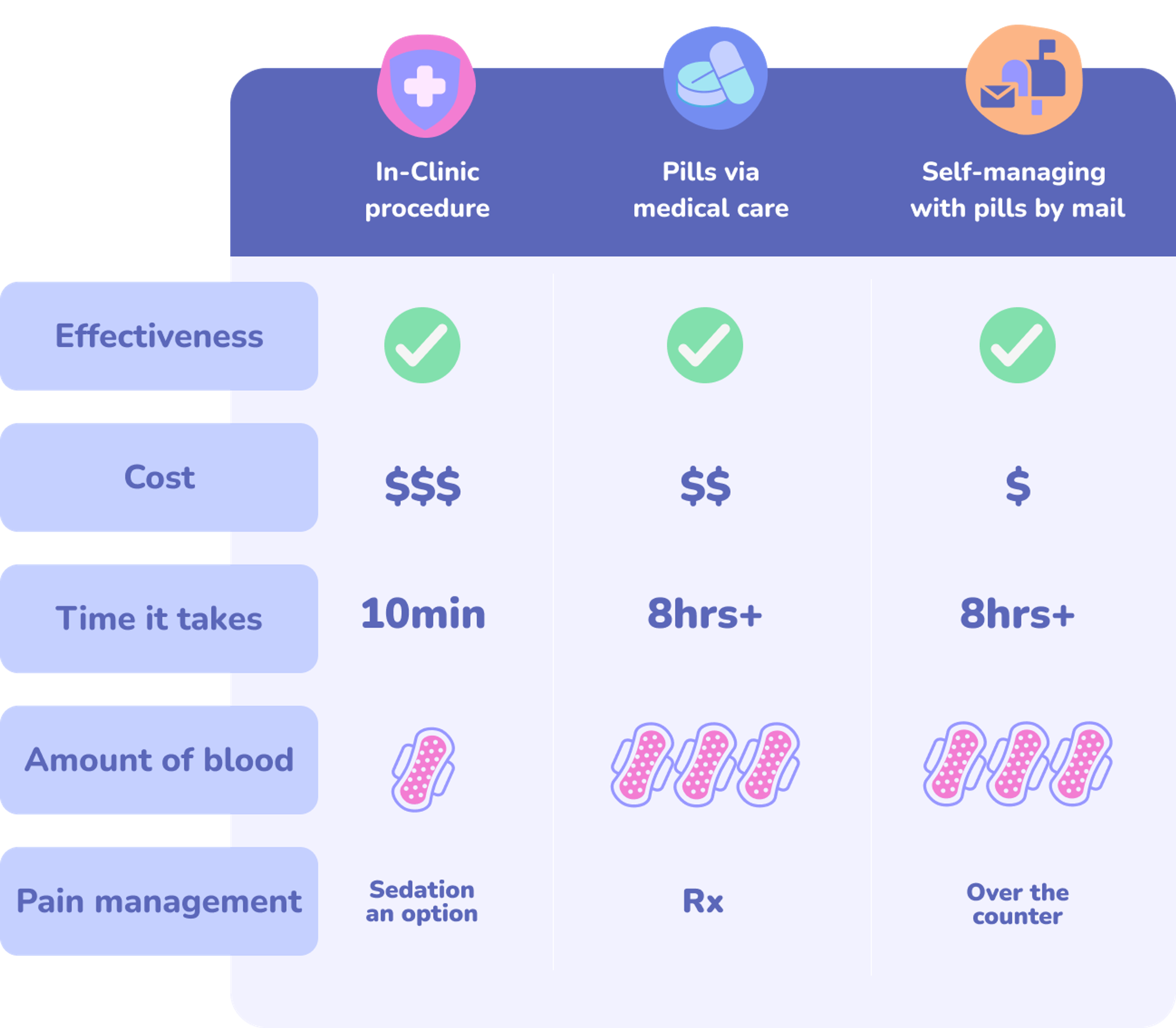
Types of Abortion
Abortions can be done either as an in-clinic procedure or with pills (medication), depending on your preference and how far along you are in your pregnancy. All types of abortion are safe and effective but they have some key differences.
In-clinic Procedure
How does it work?
With an abortion procedure, the process begins very similarly to when you have a pap smear. The doctor will do a brief pelvic exam and then insert a speculum into the vagina in order to view the cervix. The doctor will numb the cervix with an injection of lidocaine. Then, they will gradually dilate the cervix in order to insert a narrow flexible tube into the uterus, called a cannula. The cannula is connected to a vacuum that will then remove the pregnancy tissue with gentle suction. The suction portion takes about one minute and the entire procedure takes around 5 to 10 minutes.
Everyone has a different experience and pain tolerance; some people have described the cramping and pain as mild while others have explained it as more severe. The cramping occurs as the cervix is stretched open and as the uterus is being emptied because it contracts to get smaller. Some clinics offer pain or sedation medications to help, however they will require you to have a ride home if given sedation. Be sure to ask them before you arrive about your options for sedation. Due to required exams, filling out paperwork, time in the recovery room, and waiting in between, patients tend to spend several hours at the clinic.
- Check out this video by Safe2choose for a more detailed description of the procedure
- Check out stories from people who've had in-clinic abortions.
Medication Abortion Under Physician Care
How does it work?
Typically, medication abortion or abortion pills are a combination of two medications: mifepristone and misoprostol. This is what clinics all over the country currently offer.
These medications can be distributed by a doctor at a clinic or via telemedicine in states where abortion is legal. The first medication, mifepristone, is usually swallowed at the doctor's office. This pill is designed to block progesterone, a hormone that supports early pregnancy. The second medication, misoprostol, will be given by the doctor or a pharmacy to take at home or a safe place of your choosing 24-48 hours after the first pill. Misoprostol is typically placed in between the lip and the gums, in the vagina, or under the tongue and will induce bleeding, cramping and the passing of the pregnancy.
Usually, the heaviest bleeding and cramping will occur within the first 4-6 hours hours after taking misoprostol, but you may continue to experience some bleeding for several days or even weeks. Doctors may prescribe pain medications for the cramping but taking ibuprofen or Tylenol is helpful!
- Check out Planned Parenthood’s more detailed description of the medication abortion.
- Check out stories from people who have taken abortion pills.
Abortion Pills by Mail / Self Managing Abortion
How does it work?
Even though some states restrict abortion pill access, there are several ways people still get abortion pills by mail in all 50 states. Some people get pills from online clinics like The MAP or Abuzz. Some people get abortion medications for free from community networks like Las Libres or AccessMA. While taking abortion pills outside of a formal medical context is safe and effective, it may come with legal risk for the pregnant person and their support system. The process of taking mifepristone and misoprostol is exactly the same as if you went to the doctor, except the medications will be sent in the mail or given to you in person by community networks.
Alternatively, an abortion with medication can be effective with only misoprostol but the process is slightly different. This requires taking 12 misoprostol total -- 4 pills are placed in between your lip and your gum or under your tongue and you repeat this process every 3 hours.
Taking ibuprofen and using a heating pad can help with the pain and cramping. Clinics usually do not offer medication abortions if you’re over 12 weeks but many people all across the world have abortions with pills at home later in pregnancy. Studies show taking abortion pills after 12 weeks can be safe and effective. At this gestational age an abortion with pills can take longer, requires multiple doses of misoprostol, and ends with pregnancy tissue that is more developed (usually a fetus + placenta). Read more about taking abortion pills after 12 weeks.
- You can read more instructions for the medication abortion at home at the Miscarriage + Abortion Hotline.
- Check out stories from people who have self managed their abortion.
You can learn more about how we think about legal risk here. If you have any questions or concerns, we recommend calling the Repro Legal Helpline at 844-868-2812 to talk with a lawyer about your specific legal risk.
Price Comparison
Use our trip estimate calculator
“What if….?”
More comparisons and stories
Everyone has different experiences, preferences and circumstances so the method you choose is the right one for you! If you’re still unsure about the best method check out r/abortion - how to decide between the surgical and medical abortion or call or text the Reprocare Healthline at (833) 226-7821 and talk to someone.
Comparing Types of Abortions
In-Clinic Abortion
Medication Abortion Under Physician Care
Abortion Pills by Mail / Self-Managing Abortion
Where does the abortion take place?
At a clinic.
Where does the abortion take place?
The mifepristone is taken at the clinic.
The misoprostol is taken at home or a safe place of your choosing.
Where does the abortion take place?
At home or a safe place of your choosing.
Will a doctor be there?
A doctor will perform the procedure while the nurse monitors your vitals.
After the abortion, you’ll have access to the 24 hour nurse line at the clinic or you can speak to a doctor at the M+A Hotline.
Will a doctor be there?
A doctor or midwife will administer the mifepristone in the clinic.
At home, when you take the misoprostol, you’ll have access to the 24 hour nurse line or you can speak to a doctor at the M+A Hotline.
Will a doctor be there?
You can speak to a doctor at the M+A Hotline.
If you are using telemedicine services, you can speak to a doctor or nurse
Who can be there with me?
Typically in the exam room there will be the doctor, nurse and medical assistant.
If you bring a friend, partner or relative they will need to stay in the waiting area.
Who can be there with me?
The first medication (mifepristone) is taken in front of the doctor.
You can have whomever you’d like with you for the second medication (misoprostol) or have your own privacy if you prefer.
Who can be there with me?
You can have whomever you’d like with you when you take the medications or have your own privacy if you prefer.
How soon can I have abortion?
Depends on the clinic appointment availability (typically during the week, but they may have Saturday appointments). Plan to be at the clinic for several hours.
How soon can I have abortion?
The mifepristone usually must be taken in the clinic so it depends on clinic availability.
You can take the misoprostol 24-48 hours later at a time that’s convenient for you -- after work, after the kids go to bed, etc.
How soon can I have abortion?
If you are having pills mailed to you, it could take a few days for them to arrive.
Once you have the medication, it can be taken at a time that works best for your schedule -- after work, after the kids go to bed, etc.
What's the cost? Is there financial aid?
The cost of in-clinic abortions can vary between $450 to several thousand depending on how long you've been pregnant. Some clinics can accept private insurance or help you connect with state medicaid. Most clinics will also be able to connect you with a local abortion fund.
What's the cost? Is there financial aid?
Abortion pills via a medical provider can range from $150 - $700. Like in-clinic procedures, many providers can help you navigate how to pay for your abortion via insurance or state funding. If that's not an option, they may be able to connect you with a local fund.
What's the cost? Is there financial aid?
The costs to receive pills by mail are often less than via a clinic. The average price is $150, but many services offer sliding scale or free abortion pills based on need.
What’s the risk of something going wrong?
When instruments and suction are inserted into the vagina and uterus, there is a less than 1% risk of cervical injury or uterine perforation, which may necessitate additional medical treatment or abdominal surgery.
What’s the risk of something going wrong?
There is a 2-5% chance the pills could fail which may require an aspiration procedure to complete the abortion. When instruments and suction are inserted into the vagina and uterus, there is a less than 1% risk of cervical injury or uterine perforation
What’s the risk of something going wrong?
There is a 2-5% chance the pills could fail which may require an aspiration procedure to complete the abortion. When instruments and suction are inserted into the vagina and uterus, there is a less than 1% risk of cervical injury or uterine perforation